ISO 9001 Quality Management System - Training Courses
In our current globalized economy and complex supply chains, John Ruskin’s adage, “Quality is never an accident. It is always the result of intelligent effort” is even more relevant today than it was on the day he said it. Organizations cannot rely on chance and hope to deliver quality products and services; instead, they must establish a consistent and planned approach for managing quality. With over one million certified organizations worldwide, ISO 9001 remains the world’s most well-known standard, which provides organizations with a structured approach for quality management and helps them consistently provide products and services that meet and, where possible, exceed customer requirements.
What is ISO 9001?
Published initially in 1987, ISO 9001 is the first international management system standard (MSS) that specifies the requirements for the establishment, implementation, operation, maintenance, and continual improvement of a quality management system (QMS) in an organization.
ISO 9001 is based on seven quality management principles and it aims to help organizations be more efficient and improve customer satisfaction. A common misconception is that ISO 9001 is intended for larger companies and manufacturers. However, the requirements of ISO 9001 are generic and applicable to any organization, regardless of its type, size, or the products or services it provides.
Why is ISO 9001 important for organizations?
Ever since its initial publication, ISO 9001 has been the most recognized and widely used management system standard. A QMS based on ISO 9001 enables organizations to ensure success in the long term. In addition, a certified QMS provides additional assurance to customers and business associates, which further improves the business of an organization.
Even though ISO 9001 sets the minimum requirements that must be met, it still allows organizations to tailor the QMS to their needs. Thus, organizations should determine their overall context in order to identify issues, constraints, and opportunities that are specific to their context. In addition, they should set objectives and establish processes which contribute to the achievement of those objectives.
A distinct feature of a QMS based on ISO 9001 is that it puts customers first. “Meeting customers’ needs and exceeding their expectations” is engraved in the quality management principles, and is implied continuously on the requirements stated in clauses 4 to 10 of the standard. As such, organizations that implement and establish a QMS based on ISO 9001 will maintain the focus on their customers by continuously identifying their needs and requirements, obtaining feedback from them, and continually improving their products and services to fulfill their needs. This focus on customer satisfaction is one of the key factors that have allowed the ISO 9001 to achieve the landmark status.
Like most of the management system standards, ISO 9001 is structured according to the High-Level Structure (HLS) and shares the common terms and core definitions. This alignment enables an easier integration with other management systems based on standards such as ISO 14001, ISO/IEC 20000-1, ISO/IEC 27001, ISO 22301, etc. Apart from ensuring consistency and reducing costs, integrating several management systems can improve the organization’s ability to successfully address other organizational commitments.
Benefits of ISO 9001 for organizations
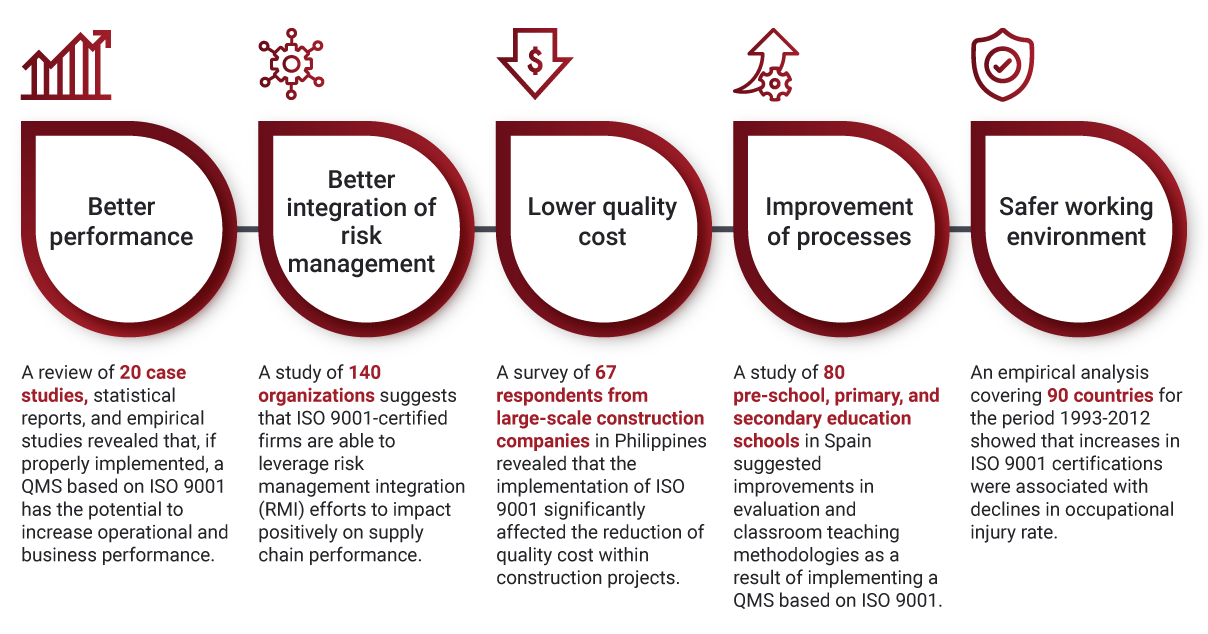
Benefits of implementing a QMS based on ISO 9001
Why should you attend one of our ISO 9001 training courses?
While ISO 9001 can be used by organizations to obtain many benefits, many organizations are unable to fully realize the benefits of a QMS implementation. There are different factors which contribute to the inability to integrate the QMS into the organization’s processes. Such factors include, but are not limited to:
- The perception of the QMS as a system of documentation.
- The inability to identify nonconformities.
- The inability to ensure continual improvement.
PECB’s training courses, both lead implementer or lead auditor, are tailored to overcome such challenges.
Globally recognized, PECB certifications demonstrate an individual’s professional capabilities to contribute in an organization’s QMS, as an auditor, implementer, or QMS implementation team member.
Obtaining a certificate in ISO 9001:
- Distinguishes you from other quality management consultants/auditors
- Demonstrates your awareness and knowledge of an internationally recognized standard for the management of quality in organizations
- Demonstrates that you have the necessary competencies to guide and support organizations through the implementation and management of a QMS (PECB Certified ISO 9001 Lead Implementer)
- Demonstrates that you have the necessary competencies to assess the conformity of a QMS against the requirements of ISO 9001 and the organization’s own requirements (PECB ISO 9001 Lead Auditor)
- Qualifies you to conduct third-party certification audits on behalf of conformity assessment bodies (PECB ISO 9001 Lead Auditor)
- Provides you with opportunities to further improve your career in quality management, either as an auditor, implementer, or a member of auditing/implementation team